Farmers rely on tractors for critical tasks, but many struggle with maintenance due to a lack of understanding of key components. Without this knowledge, costly breakdowns and inefficiencies arise.
A farm tractor consists of seven essential systems: engine, transmission, chassis, hydraulics, PTO, control systems, and electrical system. Each part plays a key role in power delivery, operation, and implement handling.
Knowing these fundamental parts helps with maintenance, troubleshooting, and optimizing performance. Let's break down each one.
A farm tractor consists of seven essential systems.True
The seven key systems of a farm tractor are engine, transmission, chassis, hydraulics, PTO, control systems, and electrical system.
Each part of a tractor has minimal impact on its overall operation.False
Every component, from the engine to the control systems, plays a crucial role in power delivery, operation, and implement handling.
1. Engine
I see the engine as the most important part of a tractor. Without it, the machine cannot move, lift, or operate any farm implements. The engine generates the power needed for every function, from plowing fields to towing heavy loads.
Most farm tractors use diesel engines because they produce high torque at low speeds1. This means they can pull heavy equipment and handle tough field conditions without stalling. Diesel engines are also more fuel-efficient than gasoline engines, making them cost-effective for long hours of operation.

How the Engine Works
A tractor engine works by burning fuel to create mechanical power. This power is transferred to the transmission system, which then moves the wheels and powers various implements.
| Key Feature | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| High Torque | Provides strong pulling power for plowing and towing heavy loads. |
| Fuel Efficiency | Uses less fuel while delivering consistent power. |
| Durability | Designed to handle long hours of work in tough conditions. |
| Cooling System | Prevents overheating and keeps the engine running smoothly. |
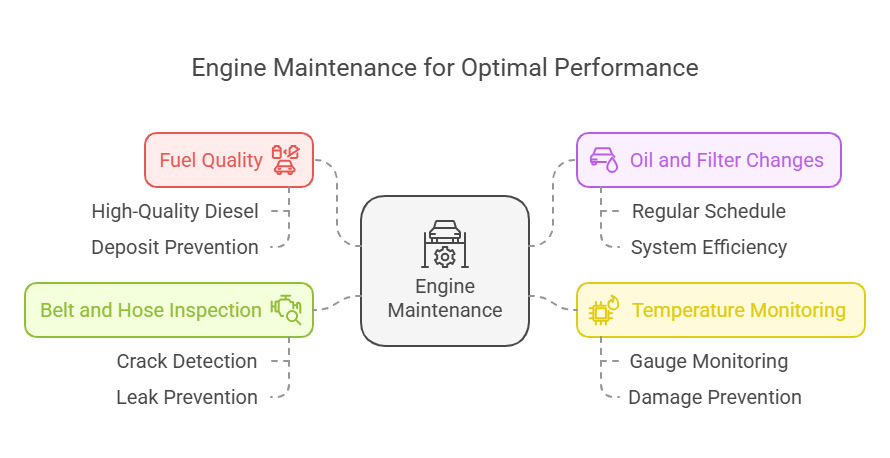
Why Regular Engine Maintenance is Critical
A well-maintained engine lasts longer, performs better, and prevents costly breakdowns. To keep it in top condition:
- Use high-quality diesel fuel to prevent deposits from clogging the system.
- Change the oil and filters regularly to keep the engine clean and running smoothly.
- Monitor temperature gauges to avoid overheating, which can cause serious damage.
- Inspect belts and hoses for cracks or leaks that could lead to failures.
Ignoring engine maintenance can result in power loss, increased fuel consumption, and unexpected downtime. A healthy engine ensures the tractor runs efficiently, keeping farm operations smooth and productive.
Diesel engines are more fuel-efficient than gasoline engines in tractors.True
Diesel engines produce high torque at low speeds and consume less fuel per unit of work, making them more cost-effective for long hours of operation.
Tractor engines do not require regular maintenance.False
Regular maintenance, such as oil changes and monitoring temperature gauges, is essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent costly breakdowns.
2. Transmission System
I know that a powerful engine alone isn’t enough—a tractor needs a strong transmission system to transfer that power where it’s needed. Without a good transmission, the engine’s energy is wasted2, and the tractor cannot move or perform its tasks efficiently.
The transmission system connects the engine to the wheels and other working parts of the tractor. It allows me to control speed, change direction, and operate smoothly across different terrains.

Key Components of Transmission System
The transmission system is made up of several parts that work together to control movement. Each plays a crucial role:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Clutch | Connects and disconnects the engine from the transmission, making gear shifts smooth. |
| Gearbox | Adjusts the tractor’s speed and direction to match different tasks. |
| Differential | Allows the wheels on the same axle to rotate at different speeds for stable turns. |
How the Transmission System Works?
When I press the clutch pedal, it disconnects the engine from the transmission, allowing me to change gears smoothly. Once I select a gear and release the clutch, power flows from the engine through the gearbox to the wheels.
- Lower gears provide more power but less speed—perfect for plowing or towing.
- Higher gears allow for faster movement with less power, ideal for transporting loads.
- The differential helps with turning by letting the inner and outer wheels rotate at different speeds. This prevents slipping, especially on rough terrain.
Transmission Maintenance Tips for Smooth Operation
A poorly maintained transmission can cause jerky movements, power loss, or complete failure. To prevent issues, I always:
- Check and change transmission fluid3 regularly to keep gears lubricated.
- Engage the clutch smoothly to avoid sudden wear and tear.
- Inspect gears for grinding noises—a sign of wear or misalignment.
- Ensure the differential4 is working properly to maintain smooth turning.
A well-maintained transmission system ensures precise control, smooth operation, and long-lasting performance. Without it, my tractor wouldn’t be able to handle different tasks effectively.
A tractor’s transmission system transfers engine power to the wheels and other working parts.True
The transmission system ensures that engine power is efficiently distributed, allowing the tractor to move, change speeds, and operate implements.
Higher gears provide more power for plowing and towing.False
Lower gears provide more power but less speed, making them ideal for plowing and towing, while higher gears prioritize speed with less power.
3. Chassis
I see the chassis as the foundation of a tractor. Without a strong chassis5, all other components—engine, transmission, and hydraulics—would have nowhere to sit. A weak or damaged chassis can lead to instability, poor traction, and even dangerous breakdowns in the field.
The chassis is the structural frame6 that holds everything together. It supports the engine, axles, wheels, and other critical systems while ensuring the tractor stays balanced under heavy workloads.

Key Components and Functions of the Chassis
Each part of the chassis plays a vital role in keeping my tractor stable and efficient:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Frame | The main body of the tractor, supporting all mechanical parts. |
| Axles | Connects and holds the wheels, allowing power transfer from the transmission. |
| Wheels & Tires | Large rear wheels provide traction, while smaller front wheels help with steering. |
How the Chassis Works to Keep My Tractor Stable
The frame is the most critical part. It absorbs stress from rough terrain, heavy loads, and continuous vibrations. Without a sturdy frame7, cracks can develop, leading to instability.
The axles connect the wheels to the chassis and support weight distribution8. The rear axle carries most of the load, especially when pulling implements, while the front axle assists in steering.
The wheels and tires determine traction and stability9. Large rear tires with deep treads help grip the ground, preventing slippage in muddy or uneven fields. Meanwhile, the smaller front wheels allow precise steering.
How to Maintain Tractor’s Chassis for Longevity?
A damaged chassis can lead to poor handling, misaligned wheels, and reduced power transfer. To prevent this, I always:
- Inspect the frame for cracks or rust, especially after working on rough terrain.
- Check axle alignment to ensure smooth power transfer and prevent uneven tire wear.
- Monitor tire pressure and tread depth to maintain proper traction and balance.
- Lubricate moving parts to reduce wear on axles and suspension components.
A strong chassis ensures tractor remains durable, stable, and reliable for years, even under the toughest working conditions.
The chassis is the structural frame that holds all major tractor components together.True
The chassis supports the engine, transmission, axles, and other critical systems, ensuring stability and durability under heavy workloads.
The front axle carries most of the tractor's load when pulling implements.False
The rear axle carries most of the load, especially when pulling implements, while the front axle primarily assists with steering.
4. Hydraulic System
From lifting a plow to adjusting a loader, my tractor’s hydraulic system makes everything easier. Without it, moving heavy implements or controlling attachments would require much more effort and time.
The hydraulic system uses pressurized fluid to generate force, allowing me to lift, lower, and adjust implements with precision. It’s what enables tractors to handle front loaders, backhoes, and other essential farm equipment.
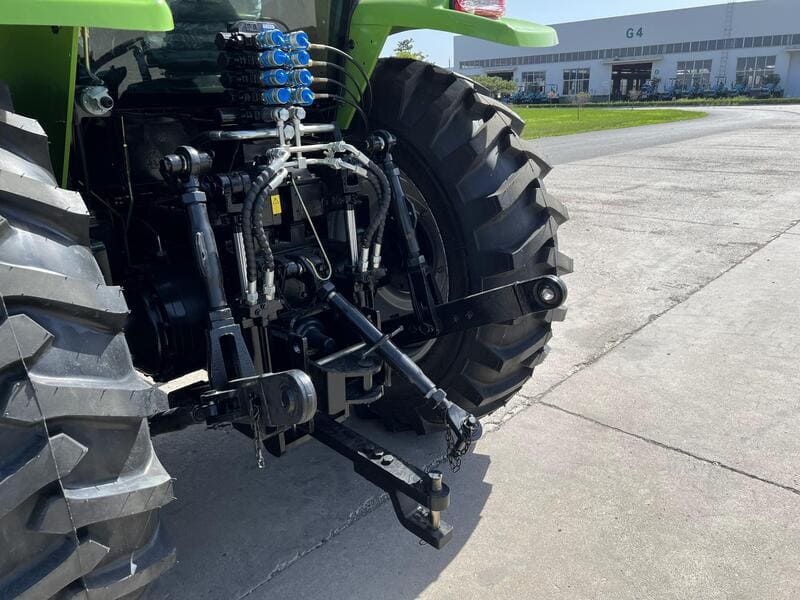

Key Components of the Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system relies on several crucial parts to function properly:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Hydraulic Pump | Pressurizes the hydraulic fluid, creating the force needed to operate implements. |
| Hydraulic Cylinders | Convert hydraulic pressure into mechanical movement, allowing lifting and adjustment. |
| Linkage Controls | Allow me to raise, lower, and adjust attachments with precision. |
How the Hydraulic System Works?
When I activate the hydraulics, the hydraulic pump10 draws fluid from a reservoir and pressurizes it. This pressurized fluid travels through hoses to the hydraulic cylinders11, which extend or retract based on the control inputs.
- Lifting a front loader: The cylinders push the arms upward, raising the implement.
- Lowering a plow: The cylinders release pressure, allowing the plow to move downward.
- Adjusting an attachment’s angle: The linkage controls fine-tune the position for better accuracy.
Since hydraulic systems12 work under high pressure, even a small leak can reduce efficiency or lead to system failure.
How to Maintain Hydraulic System?
A poorly maintained hydraulic system can lead to slow response times, weak lifting power, and fluid leaks. To keep mine in top shape, I always:
- Check hydraulic fluid levels regularly to ensure smooth operation.
- Inspect hoses and fittings for leaks or cracks—even a small leak can affect performance.
- Replace hydraulic filters as needed to keep contaminants out of the system.
- Avoid overloading the system by keeping within the recommended weight limits for attachments.
When hydraulics are in top condition, you can control my implements easily, improve efficiency, and reduce wear on farm tractor. A reliable hydraulic system is essential for modern farming.
A tractor’s hydraulic system uses pressurized fluid to lift, lower, and adjust implements.True
The hydraulic system relies on a pump to pressurize fluid, which moves through hoses to hydraulic cylinders, enabling precise control of attachments.
Hydraulic systems in tractors do not require regular maintenance.False
Regular maintenance, such as checking fluid levels, inspecting hoses for leaks, and replacing filters, is essential to ensure smooth operation and prevent failures.
5. Power Take-Off (PTO)
One of the biggest advantages of using a tractor is its ability to power external implements like mowers, balers, and augers. This wouldn’t be possible without the Power Take-Off (PTO) system13.
The PTO transfers mechanical power from my tractor’s engine to attached farm equipment14. Without it, many implements would require separate engines, increasing costs and complexity.

How the PTO System Works?
When I engage the PTO, my tractor’s engine sends rotational energy to a spinning PTO shaft. This shaft connects to an implement, allowing it to use my tractor’s power instead of relying on its own engine.
There are three main types of PTO systems, each designed for different needs:
| PTO Type | How It Works | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission PTO | Stops when I press the clutch because it’s directly connected to the transmission. | Basic tasks that don’t require constant PTO operation. |
| Live PTO | Operates independently of the tractor’s movement, but still relies on a two-stage clutch. | Mowing, baling, and tasks where stopping the tractor shouldn't stop the PTO. |
| Independent PTO | Fully separate from the transmission; I can engage or disengage it anytime using a lever or switch. | Continuous power-demanding implements like rotary tillers and sprayers. |
Why the PTO System is Critical for Farm Work?
With the PTO, one tractor can do the work of multiple machines. I can switch between different implements, saving both time and money. For example:
- A rotary tiller15 powered by the PTO helps prepare soil for planting.
- baler can collect and compress hay16 with my tractor supplying the necessary power.
- water pump connected to the PTO17 allows me to irrigate my fields efficiently.
Without a functioning PTO, my tractor becomes just a heavy vehicle instead of a multi-purpose farm tool.
How to Maintain My PTO for Reliable Operation?
Since the PTO operates at high speeds and torque, any damage or malfunction can lead to dangerous failures. To prevent issues, I always:
- Inspect the PTO shaft and connections regularly to ensure they are securely attached.
- Keep the PTO shaft lubricated to reduce friction and wear.
- Use the correct PTO speed (measured in RPM) to match each implement’s requirements.
- Check PTO guards and shields for damage to ensure safety during operation.
A properly maintained PTO system extends the life of my tractor and implements, improving overall efficiency on farm.
The Power Take-Off (PTO) system allows a tractor to power external implements.True
The PTO transfers mechanical power from the tractor’s engine to attached equipment, enabling implements like mowers, balers, and pumps to operate without their own engines.
A tractor’s PTO system operates independently of the engine.False
The PTO relies on the tractor’s engine to generate rotational energy, which is then transferred to the implement through a spinning shaft.
6. Control Systems
A tractor’s power is useless without precise control. Whether I’m steering through tight rows, braking on a slope, or adjusting an implement’s height, the control systems allow me to operate my tractor safely and efficiently.
The control system includes the steering, braking, and operator controls that allow to maneuver and manage every function of my tractor with ease.
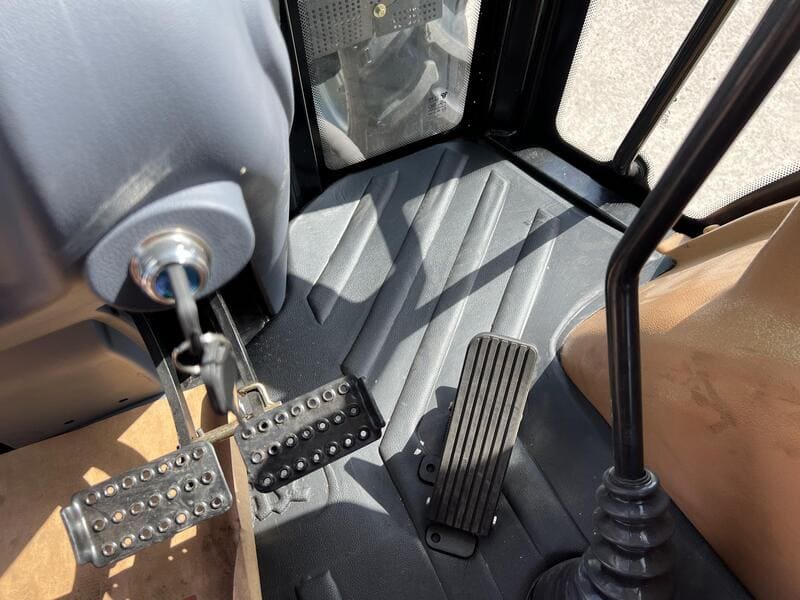

Key Components of the Control System
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Steering System | Allows me to control the direction of my tractor by adjusting the front wheels. |
| Braking System | Slows down or stops my tractor, ensuring safety and stability. |
| Cab and Controls | The operator’s station where I manage speed, power, and implement operation. |
Steering System: How to Keep Tractor on Course?
The steering system18 governs the movement of the front wheels, allowing me to navigate the tractor smoothly. It’s especially important when working in tight spaces or on uneven terrain.
- Manual Steering (Older Tractors): Requires more effort and relies on mechanical linkages.
- Power Steering (Modern Tractors): Uses hydraulics to reduce steering effort, making operation easier.
If my steering system fails, controlling the tractor becomes nearly impossible, especially at high speeds or with heavy loads. That’s why I check for:
- Loose or worn steering linkages that can cause misalignment.
- Hydraulic leaks in power steering systems that make the wheel harder to turn.
- Proper tire inflation to ensure balanced steering performance.
Braking System: Ensuring My Tractor Stops Safely
A strong braking system is critical when working on slopes, transporting heavy loads, or making precise turns. Tractors use two main types of brakes:
| Brake Type | How It Works | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Brakes | Uses friction between brake shoes and a drum. | Lighter-duty applications, older tractors. |
| Wet Brakes | Uses oil-cooled discs inside a sealed system. | Heavy-duty work, longer-lasting performance. |
If brakes fail, the tractor could roll uncontrollably, leading to serious accidents. That’s why I always:
- Check brake pedal resistance—soft or spongy pedals indicate fluid leaks.
- Listen for unusual noises when braking, which could mean worn-out components.
- Inspect hydraulic fluid levels for wet brake systems.
Cab and Controls: My Command Center
The operator’s station is where I control every aspect of my tractor’s performance. A well-designed cab makes my work easier, more efficient, and more comfortable.
Inside my tractor’s cab, I manage:
- The steering wheel for direction19.
- Throttle and gear levers for speed and power control.
- Instrument panel displaying engine temperature, fuel levels, and PTO speed.
- Hydraulic levers to adjust and control attached implements.
Some modern tractors also come with GPS guidance20, touchscreen displays, and automated controls to improve precision and efficiency.
How to Maintain Control Systems?
A faulty control system can lead to poor handling, longer stopping distances, and decreased efficiency. To keep everything working smoothly, I always:
- Check steering fluid levels and linkages for smooth movement.
- Inspect and test brakes regularly to ensure safe stopping power.
- Keep the cab clean and free of obstructions to access all controls easily.
When tractor control systems are in top condition, you can operate my tractor with confidence, safety, and efficiency, no matter the task.
The control system allows a tractor operator to steer, brake, and manage functions efficiently.True
The control system includes steering, braking, and operator controls, ensuring precise maneuverability and safe operation.
Modern tractors rely only on manual steering systems.False
Many modern tractors use power steering, which utilizes hydraulics to reduce steering effort and improve ease of operation.
7. Electrical System
A tractor’s mechanical power means nothing if it can’t start, can’t provide lighting, or can’t monitor performance. That’s where the electrical system comes in.
The electrical system provides power for the tractor’s ignition, lights, dashboard, sensors, and various electronic controls. Without a properly functioning electrical system, farmers wouldn’t be able to start tractor, operate lights in low visibility, or monitor engine performance.

Key Components of the Electrical System and Their Functions
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Battery | Provides initial power to start the engine and runs electrical components when the engine is off. |
| Alternator | Charges the battery and supplies power while the engine is running. |
| Starter Motor | Uses battery power to crank the engine during startup. |
| Wiring & Fuses | Distributes power to various components and protects the system from electrical overloads. |
| Lights & Indicators | Ensures visibility and safety during operation, especially at night. |
How the Electrical System Works?
When I turn the key, the battery sends power to the starter motor, which cranks the engine. Once the engine starts, the alternator takes over, supplying power to the entire system and recharging the battery.
All electrical components—such as lights, sensors, and the instrument panel—depend on this system. Modern tractors also use electronic fuel injection, GPS guidance, and digital controls, which further rely on a strong electrical setup.
Common Electrical Issues and How to Prevent Them
Since tractor’s electrical system is exposed to dust, moisture, and vibrations, failures can happen if I don’t perform regular maintenance. Common issues include:
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Weak or dead battery | Aging battery or parasitic drain | Check and replace the battery when needed. |
| Starter motor failure | Worn-out solenoid or poor connections | Inspect wiring and replace faulty components. |
| Alternator not charging | Broken belt or faulty regulator | Ensure belts are in good condition and test voltage output. |
| Blown fuses | Electrical short or power surge | Identify and fix the root cause before replacing the fuse. |
| Dim or flickering lights | Loose wiring or corroded terminals | Clean and tighten all electrical connections. |
How to Maintain Tractor’s Electrical System?
A failing electrical system means unexpected breakdowns, poor visibility, and inefficient operation. To avoid these issues, I follow these maintenance steps:
- Check battery terminals regularly for corrosion and clean them if needed.
- Test the alternator output21 to ensure it’s charging the battery correctly.
- Inspect and replace old wiring22 to prevent shorts or voltage drops.
- Ensure all lights, fuses, and indicators are working before starting work.
- Protect electrical components from excessive moisture and dirt buildup.
By keeping tractor electrical system in top shape, you can ensure tractor starts reliably, runs smoothly, and provides the power needed for all essential functions.
A tractor’s electrical system powers ignition, lights, sensors, and electronic controls.True
The electrical system supplies energy for starting the engine, operating lights, running sensors, and managing digital controls like GPS and fuel injection.
A tractor can operate normally without a functioning electrical system.False
Without a working electrical system, the tractor may fail to start, lose lighting in low visibility, and be unable to monitor engine performance through sensors and dashboard controls.
Conclusion
Understanding farm tractor parts improves maintenance, prevents breakdowns, and enhances efficiency. A well-maintained tractor leads to better farm productivity and reduced repair costs.
-
Learn how high torque at low speeds enhances tractor performance in challenging conditions, ensuring reliability and efficiency in farming operations. ↩
-
Exploring how to prevent engine energy waste in tractors can lead to better performance and lower operational costs, making your farming or construction tasks more efficient. ↩
-
Regular maintenance of transmission fluid ensures smooth operation and longevity of your tractor's transmission system. ↩
-
A properly functioning differential is crucial for smooth turning and overall tractor performance. Learn how to spot issues early. ↩
-
Understanding the importance of a strong chassis can help in selecting a tractor that ensures stability and safety during heavy workloads. ↩
-
Exploring the role of the structural frame can provide insights into how it supports and balances the tractor's components for optimal performance. ↩
-
Understanding the importance of a sturdy frame can help you maintain your tractor's stability and prevent potential accidents. ↩
-
Learning about weight distribution can enhance your tractor's efficiency and safety, especially when handling heavy loads. ↩
-
Exploring the role of wheels and tires can improve your tractor's performance on various terrains, ensuring better safety and efficiency. ↩
-
Understanding the hydraulic pump's operation is crucial for maintaining system efficiency and preventing failures. ↩
-
Hydraulic cylinders are pivotal for the movement and control of heavy machinery, making their function essential knowledge. ↩
-
Identifying and addressing common hydraulic system issues can significantly enhance performance and longevity. ↩
-
Understanding the PTO system can significantly enhance your farming efficiency by allowing you to power various implements directly from your tractor. ↩
-
Exploring how attached farm equipment works with a tractor's PTO system can help you maximize your agricultural productivity and reduce costs. ↩
-
Discover how a rotary tiller powered by the PTO can significantly enhance your soil preparation process, making it more efficient and less labor-intensive. ↩
-
Learn about the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of using a baler with your tractor for hay collection and compression, optimizing your farming operations. ↩
-
Explore the advantages of using a water pump connected to the PTO for irrigation, ensuring your fields receive adequate water with minimal effort. ↩
-
Understanding common issues and maintenance tips can help prevent steering system failures, ensuring safer and more efficient tractor operation. ↩
-
Discover how modern steering wheel technologies enhance tractor control and operator comfort, leading to improved efficiency and safety. ↩
-
Explore the advantages of integrating GPS guidance and automated controls in tractors, including increased precision, efficiency, and reduced operator fatigue. ↩
-
Discover how to accurately test your tractor's alternator output to ensure it's charging the battery correctly and avoid unexpected breakdowns. ↩
-
Find out the steps to inspect and replace old wiring in your tractor to prevent electrical shorts and voltage drops, ensuring efficient operation. ↩